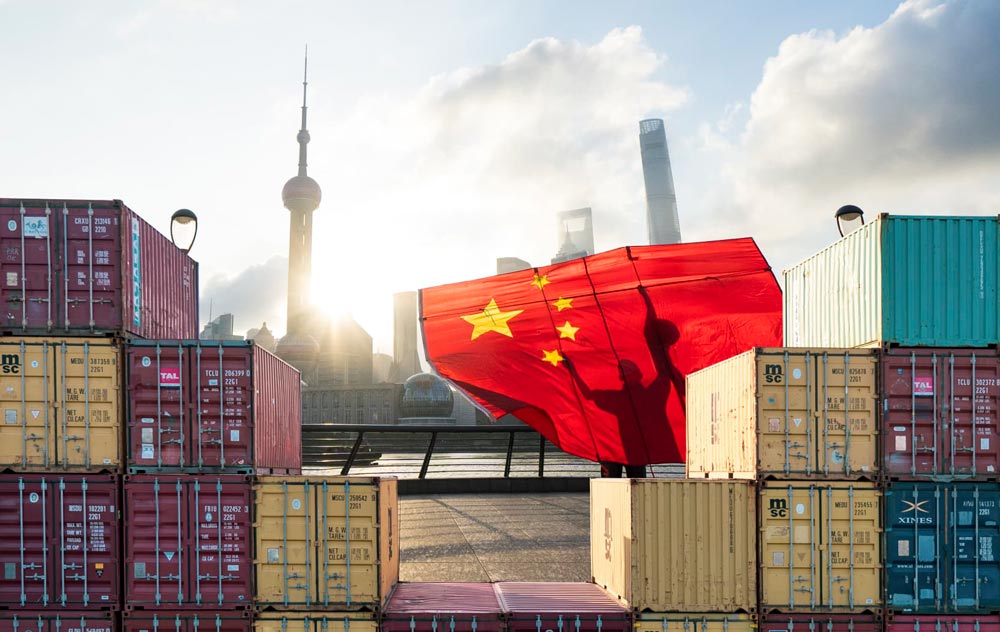
China has announced a GDP growth target of “around 5%” for 2025, reflecting its cautious optimism amidst escalating trade tensions with the United States and lingering domestic economic challenges. This goal, set during the annual session of China’s top legislative body, underscores Beijing’s focus on stabilizing its economy through fiscal stimulus and policy adjustments.
Key Measures to Support Growth
To achieve the 5% growth target, China has rolled out a series of robust stimulus measures:
Increased Budget Deficit: Beijing raised its budget deficit target to “around 4%” of GDP, up from 3% last year. This marks the highest deficit on record since 2010, surpassing the 3.6% level seen during the pandemic in 2020.
Treasury Bonds: The government plans to issue 1.3 trillion yuan ($178.9 billion) in ultra-long-term special treasury bonds in 2025, a 300 billion yuan increase over the previous year. Additionally, 500 billion yuan worth of special treasury bonds will be allocated to support large state-owned banks.
Local Government Bonds: To ease local financing pressures, Beijing will issue 4.4 trillion yuan in special-purpose bonds for local governments.
Consumer Inflation Adjustments: The annual inflation target has been revised down to “around 2%,” the lowest in over two decades. This reduction reflects China’s focus on maintaining price stability as consumer prices rose just 0.2% in 2024.
Boosting Domestic Consumption: A priority for the government, Beijing aims to expand its consumer goods trade-in program, supported by additional treasury bond funding.
Challenges Ahead
Despite these measures, officials acknowledge that achieving the 5% growth target will require “arduous work.” Domestic demand remains sluggish, and real estate investments continue to decline. Retail sales growth dropped to 3.4% in 2024, down from 7.1% in 2023, highlighting the need for stronger consumption recovery efforts.
Moreover, the ongoing trade conflict with the U.S. adds external pressure. Tit-for-tat tariffs have escalated in recent months, with the U.S. imposing additional duties on Chinese goods and Beijing responding with its own tariffs and export restrictions.
Stabilizing Employment and Exchange Rates
China aims to maintain an urban unemployment rate of around 5.5% in 2025 while creating over 12 million urban jobs. The Chinese yuan, which recently depreciated to 7.264 against the U.S. dollar, is expected to remain “generally stable at an adaptive, balanced level,” according to Chinese Premier Li Qiang.
Strategic Focus on the Private Sector and Technology
Beijing emphasized its commitment to supporting the private sector and addressing challenges posed by emerging technologies like artificial intelligence. Officials pledged to revise and improve legislation promoting the private economy, signaling a renewed focus on fostering entrepreneurial growth.
Concerns Over Sustainability
While the announcements reflect a determined push for stability, some economists remain skeptical. David Kuo, co-founder of The Smart Investor, described the 5% growth target as a “fantasy,” citing weak consumer spending and ongoing struggles in key economic sectors like real estate.