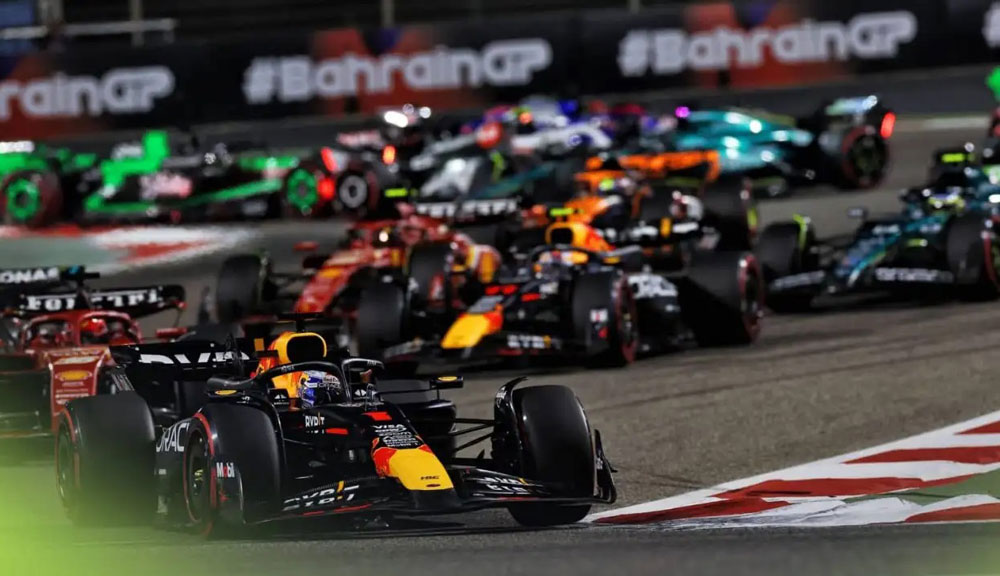
In recent years, the competition to host a Formula One Grand Prix has intensified, with countries investing billions to secure their place on the prestigious racing calendar. The allure of hosting an F1 race extends beyond the sport itself, offering significant economic and cultural benefits to host nations.
Middle Eastern Investments
Middle Eastern countries, particularly oil-rich nations, view Formula One as a critical component of their economic diversification strategies. For instance, Abu Dhabi invested a staggering $40 billion to create Yas Island, a venue specifically designed for its Grand Prix, first held in 2009. The investment has paid off, transforming the island into a major tourist destination that attracted 34 million visitors in 2023 alone.
Saudi Arabia has also leveraged Formula One to boost its tourism appeal. The nation even contemplated purchasing the sport outright to cement its status as a key player in the F1 world. A 2023 YouGov survey highlighted that U.S. race fans were more likely to visit Saudi Arabia, indicating the sport’s impact on tourism.
Global Competition
The competition to host F1 races is not limited to the Middle East. Countries like Thailand, South Korea, India, and Rwanda are making significant infrastructure investments to secure a spot on the F1 calendar. The stakes are high, as hosting a Grand Prix can add millions to a nation’s economy. Belgium, for example, benefits from an estimated $248 million annually from its race.
However, the battle for contracts is fierce. With limited slots available, not every contender can win a place. This has led to intense lobbying efforts, with some countries’ leaders personally reaching out to F1 executives.
Economic Impact and Cultural Significance
Hosting a Grand Prix brings more than just economic benefits; it also elevates the cultural status of a city. Events like the Monaco Grand Prix have become synonymous with luxury and excitement, attracting global attention. During the race weekend, local businesses often see a significant boost in revenue, with some reporting up to three months’ worth of income in just four days.
The economic value of hosting an F1 race is immense. The Las Vegas Grand Prix, for instance, generated $1.2 billion in economic activity through tourism and infrastructure investments. This “super-bowl” model of hosting races underscores the potential financial gains for host cities.
Balancing Tradition and Growth
As Formula One continues to grow, it faces the challenge of balancing its traditional fan base with new audiences. This delicate act involves making decisions about which races to add or remove from the calendar, impacting economies and fan experiences worldwide.