The Premier League, often regarded as the world’s most competitive football league, has once again proven its substantial economic contribution to the UK’s treasury. According to the 2026 “Sunday Times Tax List,” ten of the league’s top players collectively paid over £100 million in taxes last year, highlighting the significant financial impact of the sport on the nation’s economy.
Haaland Tops the List
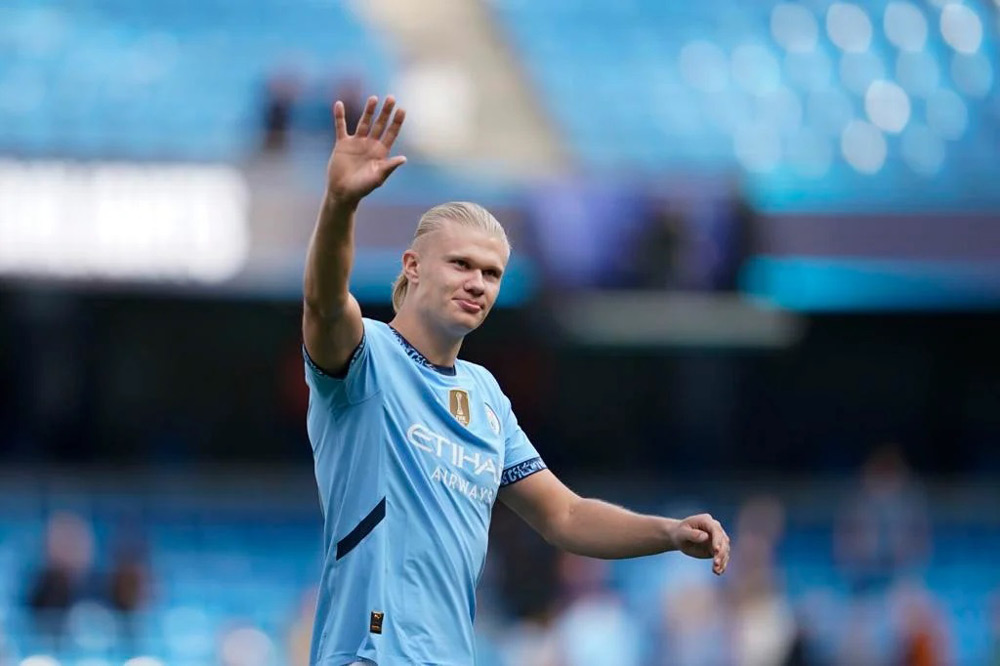
Norwegian striker Erling Haaland, who plays for Manchester City, leads the list as the highest taxpayer among the league’s stars. Haaland contributed an impressive £16.9 million in taxes, making him the top contributor in this exclusive group. Close behind him is Liverpool’s Egyptian forward Mohamed Salah, who paid £14.5 million in taxes, securing the second spot.
The Top Ten Contributors
The list continues with several other prominent names from across the Premier League:
- Erling Haaland (Manchester City) – £16.9 million
- Mohamed Salah (Liverpool) – £14.5 million
- Casemiro (Manchester United) – £10.9 million
- Raheem Sterling (Arsenal) – £9.8 million
- Virgil van Dijk (Liverpool) – £9.7 million
- Bruno Fernandes (Manchester United) – £9 million
- Bernardo Silva (Manchester City) – £9 million
- Omar Marmoush (Manchester City) – £8.8 million
- Gabriel Jesus (Arsenal) – £7.9 million
- Kai Havertz (Arsenal) – £7.8 million
A Notable Observation
One interesting detail from the list is that Raheem Sterling is the only British player among the top ten taxpayers. The remaining nine players are foreign professionals, a testament to the global appeal of the Premier League and its ability to attract top talent from around the world.
Another notable inclusion is Omar Marmoush, who recently joined Manchester City and made his debut on the list with a tax contribution of £8.8 million.
Football’s Role in the UK Economy
These massive tax contributions come at a time when the UK government is implementing stricter tax policies. British Chancellor Rachel Reeves recently announced a new budget that includes additional tax measures, potentially increasing the financial burden on high-earning athletes and clubs in the coming years.
While these policies aim to bolster the national economy, they have also sparked concerns about the Premier League’s long-term attractiveness. Analysts warn that such high taxes could prompt players to seek opportunities in other leagues with more favorable tax regimes, or force clubs to raise ticket prices to offset increased costs.
Beyond Entertainment: Football as an Economic Driver
The tax contributions of Premier League players underscore the vital role football plays in the UK’s economy. The league is not just a source of entertainment but also a significant supporter of the nation’s finances. As these figures demonstrate, the Premier League is a key player in funding public services and maintaining the country’s economic stability.